Growth Hormone
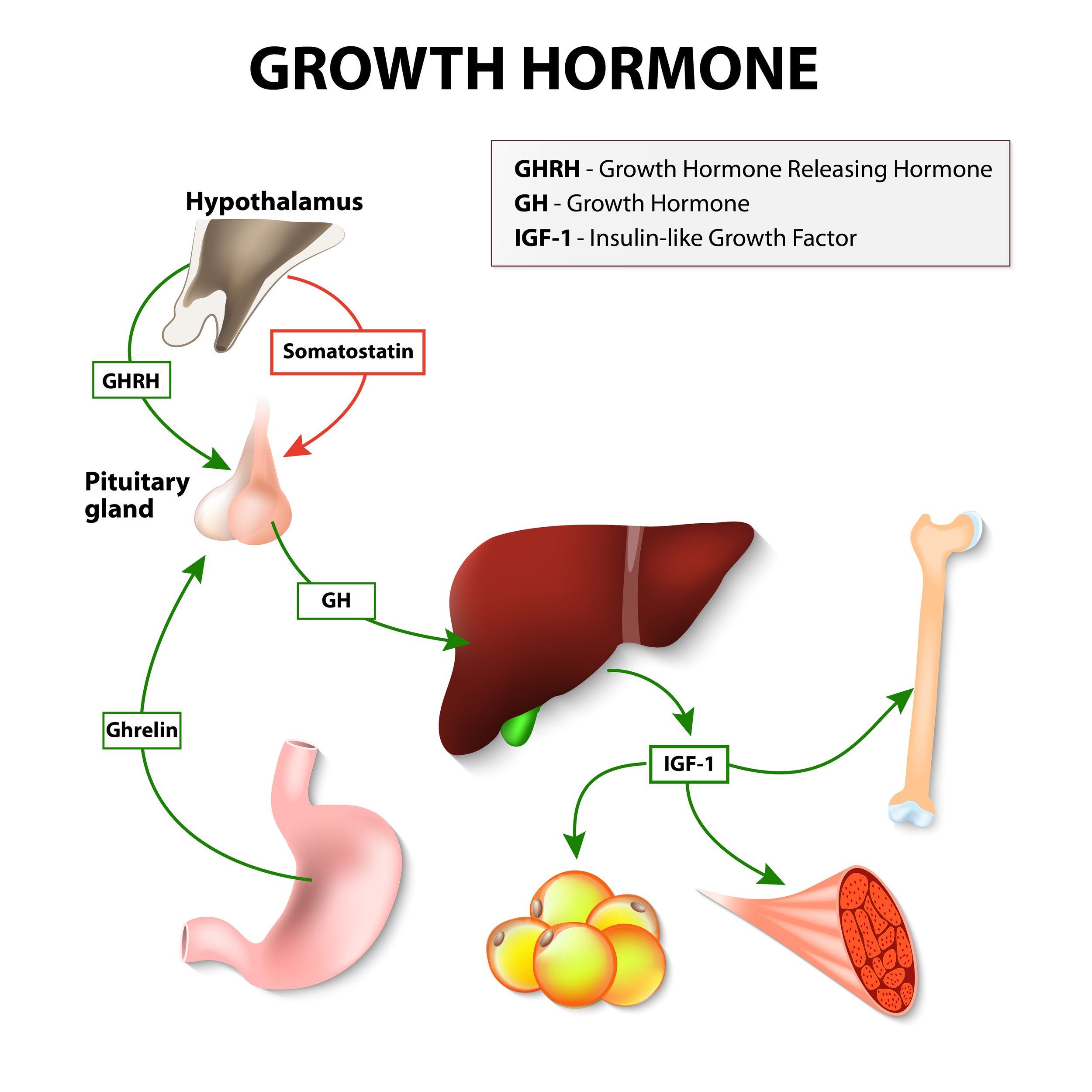
Growth hormone is released by the pituitary and has a direct effect on cells in the body. It also stimulates cells in the liver to release insulin-like-growth factors (IGF). The most common is IGF-1.
Growth hormone in adults plays a really important role around the body. It helps to maintain muscle strength, bone density, cardiac (heart) function, distribution of fat, energy levels, mood and feeling of wellbeing. It also plays an important role in regulating blood glucose levels. Some people with growth hormone deficiency experience extreme tiredness or fatigue.
Growth hormone is normally released during sleep and in times of stress.
Testing for Growth Hormone Deficiency
An Insulin Tolerance Test (ITT) is the “gold standard” test for growth hormone deficiency. This involves lowering blood glucose levels with insulin and taking blood tests to measure the response to this stress. There are contraindications for this test and so you may be offered a different test.
A GHRH-Arginine Test is another way to measure growth hormone. GHRH is the hormone from the hypothalamus that usually stimulates the pituitary to release growth hormone. In this test a synthetic version of GHRH is given to you via injection. The response from your pituitary gland is then measured in blood tests. This test has less contraindications compared to the ITT; however, it can also be less reliable.
Glucagon stress test – an alternative where an Insulin Tolerance Test (ITT) is contraindicated.
It can be difficult to accurately measure your Growth Hormone levels in a routine blood test, so IGF-1 is measured instead. This is how your Growth Hormone levels will be monitored if you start on replacement medication.
Hormone replacement for Growth Hormone deficiency
Growth hormone is a costly medication and there will be guidelines in your country to advise on its use. Like every medicine there must be a consideration of cost and benefit. Usually the greatest benefit and need is when the deficiency is severe.
In the UK, there are NICE guidelines stating what level of growth hormone deficiency qualifies for replacement medication. You can discuss this with your endocrinologist, and they will be able to advise you on the guidelines in your area.
Growth Hormone replacement is in the form of sub-cutaneous injections, usually carried out each evening. The needle is very small and goes into the fatty tissue below the skin.
There are different injector pens available depending on your country and hospital. Some may be reusable, where you attach a new needle each time and insert a cartridge of growth hormone. Some may be disposable where you use the whole unit once. You will need to be prescribed a sharps bin to safely dispose of the needles and single use units.
The growth hormone replacement is called Somatropin, and it needs to be injected because growth hormone can’t easily be absorbed in tablet form.
You will usually need to keep cartridges in the fridge when they are waiting to be used.
The cartridge in current use usually lasts for around a month out of the fridge, but you must check this with the brand you have been prescribed. If the weather is very hot this can also affect how long the cartridge will last before it goes off.
It is sensible to have a medical cool bag and ice packs for you to safely store your growth hormone in case of a power cut.
Find more information from You & Your Hormones here.
We understand that the process of testing for growth hormone deficiency and whether you will receive replacement medication can be stressful and confusing. Remember you can find support in our community.